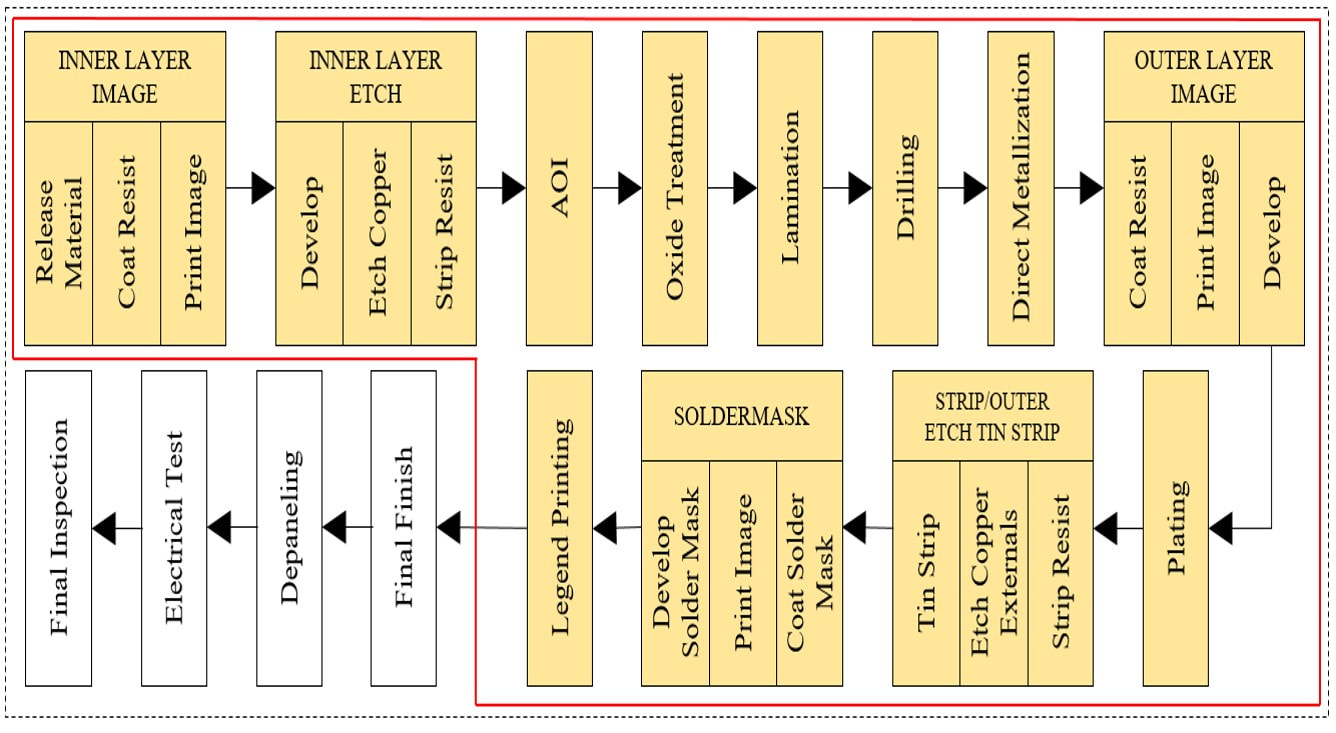
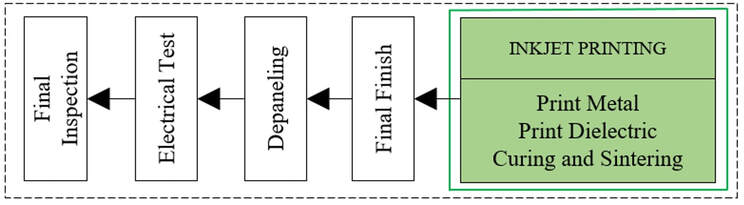
Standard PCB industrial manufacturing process
Complex, multi-stage, material intensive, costly, high waste production, environmentally aggressive, SUBTRACTIVE.
inkjetPCB
- Cheaper in terms of processing operations, materials involved, capital investment, workforce employed, waste management.
- Potentially faster (exploiting high throughput equipment).
- Increased functionalities: flexibility, passive component embedding, reduced dishomogeneities deriving from plating and etching high or low density patterned areas, etc.
- The low capex allows high parallelization in order to increase the throughput.
- Environmentally friendly: no hazardous material employed, additive manufacturing.
- Drastic reduction of factory floor plan area from 200m2 in the current state-of-the-art process to 60m2 maintaining the same throughput.
- Digital advantages: product singularization, smart production planning, change on the fly, cheap and fast prototyping.
- Non-contact process: embedding of PCBs onto 3D objects, printing of fragile substrates.
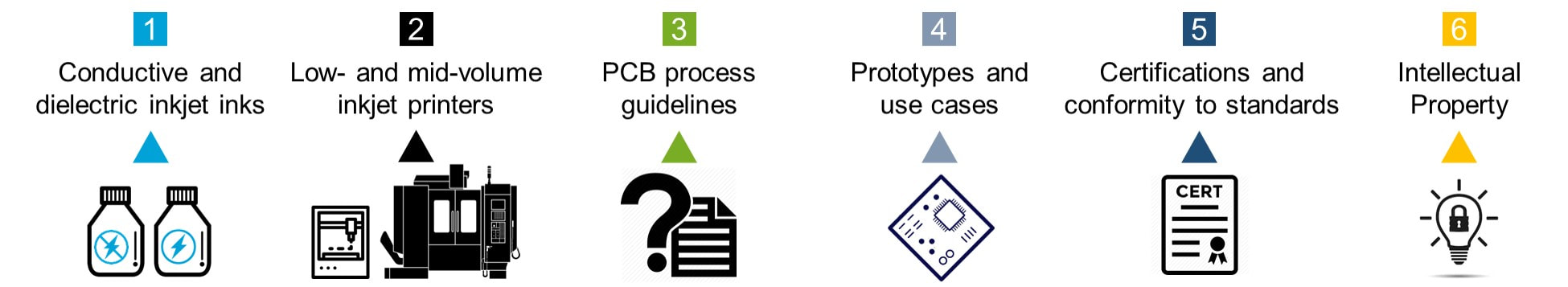
Project objectives and envisaged results
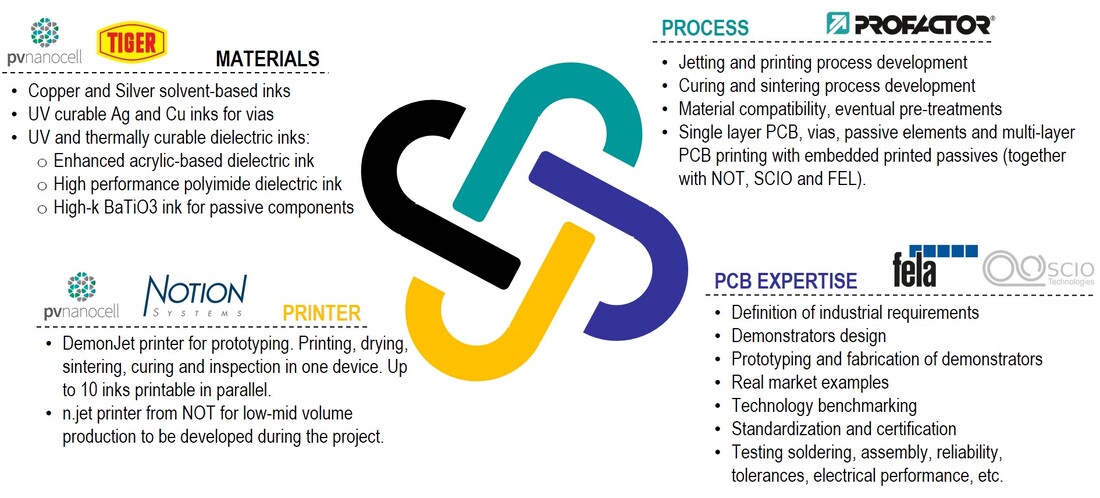
Partners & Roles
Materials: conductive and dielectric inks
- High performance polyimide dielectric ink - High-k BaTiO3 ink for passive components |
Printers: prototyping and production equipment
conductive features - Minimum conductive feature size <50µm
- UV curing - NIR laser sintering - Vision and inspection system
|